Table of content
- Executive Summary
- Understanding PPP’s Role and Limitations
- Conditions for Effective and Scalable PPP
- Identifying Key Players in the PPP Ecosystem
- Priority Topics and Areas for PPP Development
- Current Status of Public-Private Partnerships in Poland
Executive Summary
To accelerate progress towards the EU’s 2030 climate targets, innovative models of public-private partnership (PPP) are urgently needed, as no single sector can drive systemic climate transformation alone. The “Advancing Green Public-Private Partnerships” Collaborative Laboratory (CoLab), held in Warsaw, Poland on 22 October 2025, convened a diverse group of stakeholders from government, business, academia, and civil society to explore how PPPs can unlock new markets, drive adaptation, and deliver on ambitious green commitments at scale. Through collaborative dialogues in groups and panel conversation with experts, participants mapped the current PPP landscape, identified key actors and emerging priorities, and agreed on practical strategies for building trust, sharing risk, and fostering cross-sector innovation. This summary highlights the event’s core insights and actionable learning outcomes, equipping Climate KIC community members to lead the next wave of climate innovation through effective, resilient, and inclusive PPPs.
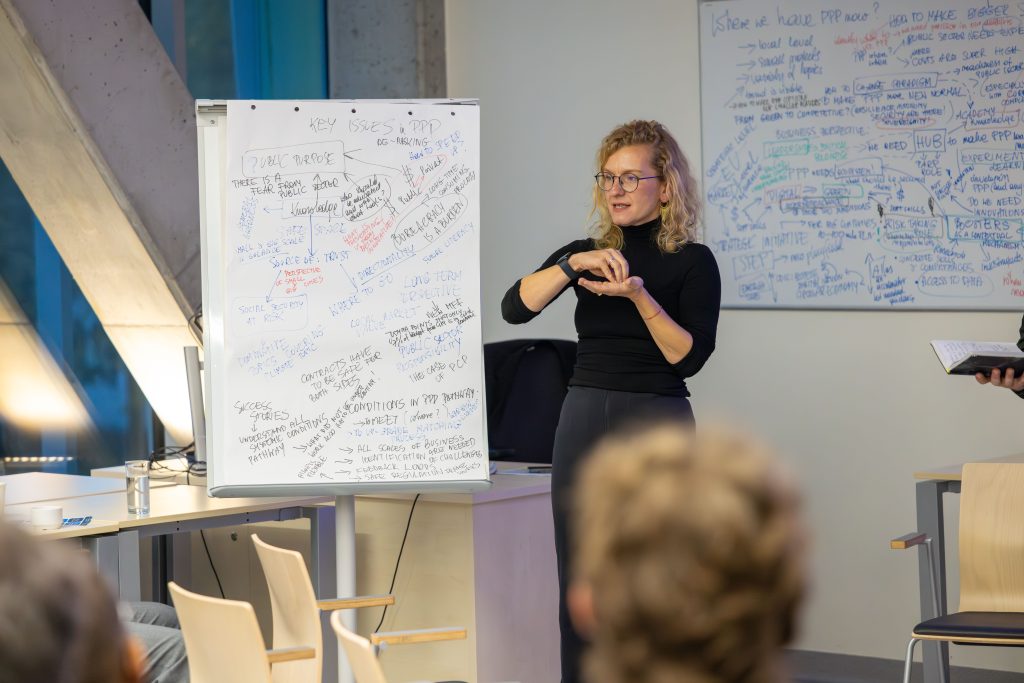
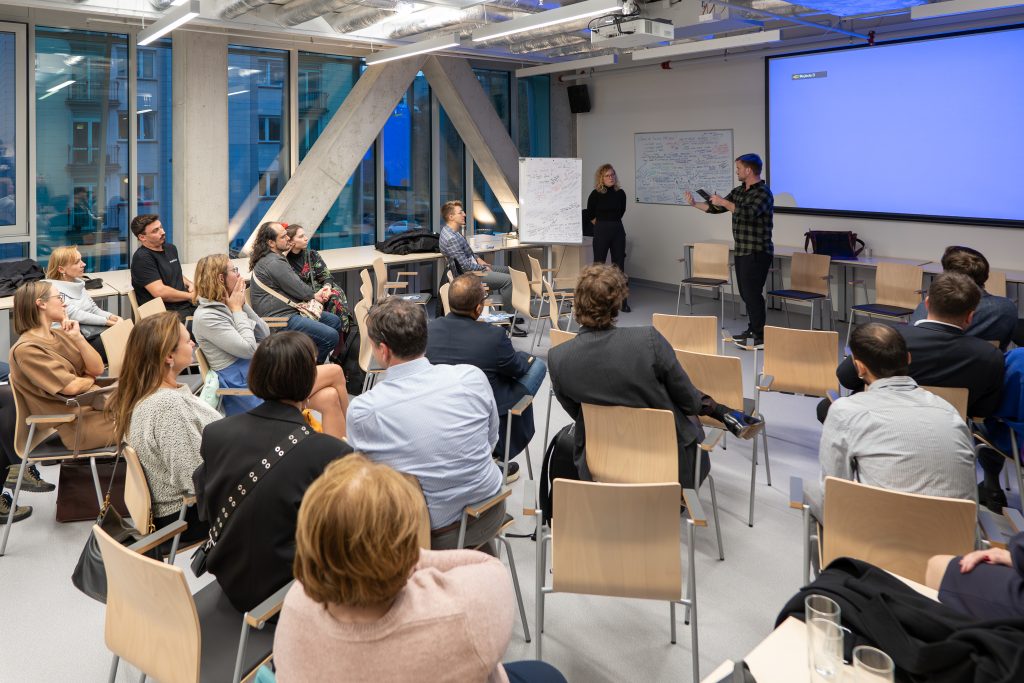

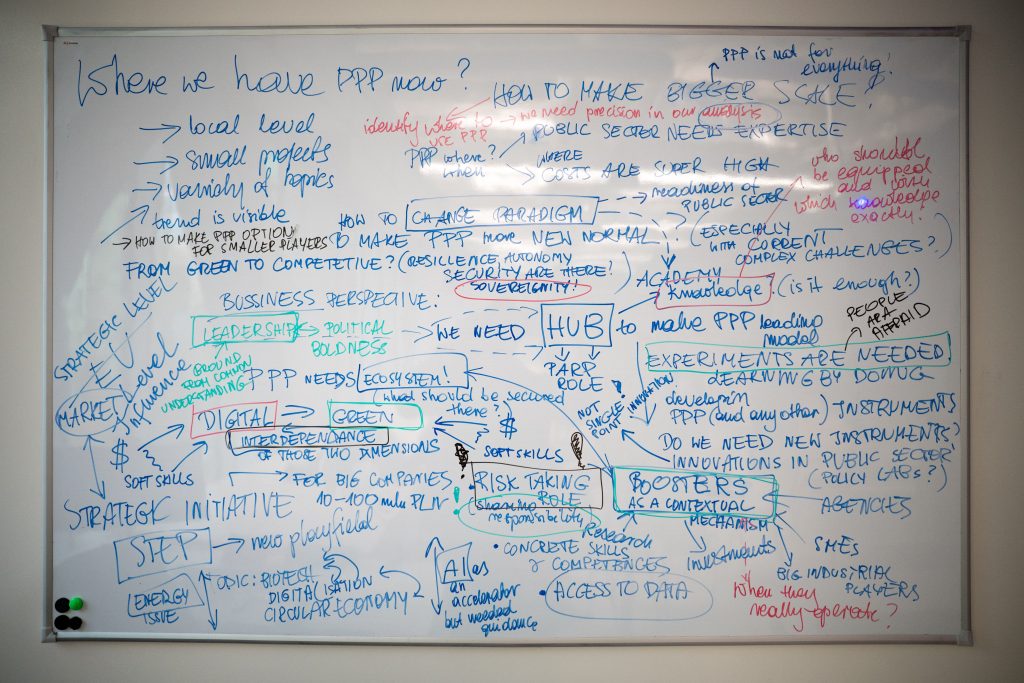



Understanding PPP’s Role and Limitations
- PPP is currently most prevalent at the local level and in smaller projects, but interest and uptake are growing.
- It is not a universal solution; its application should be context-driven.
- PPP is most effective when:
- Project costs exceed the capacity of the public sector alone.
- Complex challenges require the combined expertise of public and private actors.
Conditions for Effective and Scalable PPP
- Systems Approach: Effective PPP implementation requires a systems approach. Climate KIC and its partners are uniquely positioned to provide this expertise, supporting place-based transformation and portfolio innovation.
- EU Influence: Strategic EU-level initiatives (e.g., STEP) are shaping the PPP landscape and creating new opportunities for collaborative action.
- Common Ground: Building a shared understanding of PPP is essential, both as a specific procurement tool and as an ongoing framework for cross-sector collaboration.
- Leadership & Coordination: Strong, cooperative decision-making in both sectors is critical to overcoming barriers and enabling practical partnership.
- Continuous Knowledge Development: Ongoing learning, including tailored academies, analysis of best practices, and systemic examination of barriers, is vital to equipping stakeholders.
- Risk & Responsibility Sharing: Addressing trust gaps through clear mechanisms for sharing risk and responsibility is fundamental for successful PPPs.
- ‘HUB’ Model for Experimentation: Establishing a hub for PPP activities that includes: experimentation, knowledge-sharing, and testing of innovative approaches in diverse contexts.
- Public Sector Innovation: Greater innovation within the public sector is necessary, supported by systemic, portfolio-based interventions rather than isolated solutions.
- Access to Data: Improved data access enables effective decision-making and continuous improvement in PPP implementation.
Identifying Key Players in the PPP Ecosystem
- Public Agencies (e.g. PARP): Potential to act as central HUBs for PPP activities, coordinating efforts and knowledge exchange across sectors.
- Local Authorities: They offer diverse perspectives and are currently the main arenas where PPPs are implemented. Hence, they represent opportunities for expansion and innovation in place-based climate action.
- Business Stakeholders (from SMEs to large industry players):They bring varied experiences, resources, and sectoral insights that enrich PPP initiatives.
Priority Topics and Areas for PPP Development
- Green and Digital Transformation: Recognised as deeply interconnected and mutually reinforcing fields where PPP can drive both climate and technological innovation.
- Evolving Priorities: There is a notable shift in focus from purely “Green” objectives to those emphasizing competitiveness, resilience, safety, and autonomy. Understanding how these evolving priorities shape PPP operations is crucial for adapting strategies and ensuring that partnerships remain relevant and impactful.